Ear infections are common in children between the ages of 6 months and 3 years old. Most children have had at least one ear infection by 3 years old.
What is an ear infection?
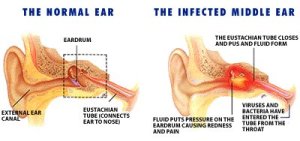
An ear infection occurs in the middle ear. The middle ear is an air filled space behind the eardrum. It is connected to the back of the nose by a small passage called the Eustachian tube.
Bacteria, viruses and fluid can enter the middle ear through the Eustachian tube and cause infection. This is often seen when a child has a cold.
Why are children more prone to ear infections?
Children are more prone to ear infections for many reasons. The passages in their ears are narrower, shorter and more horizontal than adults. This causes fluid to become trapped easier and makes it difficult to drain. Children’s immune systems are also still developing and therefore they get more colds than adults.
What are the symptoms?
- Pain or pulling the ear
- Fever
- Fussiness or irritability
- Changes in appetite or sleep
- Drainage from the ear
What is the treatment?
The symptoms of pain, fever, etc. can be treated with Tylenol or ibuprofen. For many patients the fluid within the ear will resolve on its own within 6-8 weeks. Antibiotics are often not needed for a asymptomatic middle ear fluid. If the fluid in the ear is infected and the child is symptomatic antibiotics are often prescribed.